BARITRIC SURGERY
BARITRIC SURGERY
Bariatric surgery is a weight-loss procedure that alters the digestive system to help individuals with severe obesity. This surgery can involve reducing stomach size or rerouting the intestines to limit food intake and nutrient absorption. It is recommended for those who struggle with weight-related health issues like diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea. Different types include gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding. While effective for long-term weight management, it requires lifestyle changes for success. Patients may experience temporary side effects like nausea or nutrient deficiencies. Without proper care, complications like leaks or blood clots can occur. Early medical evaluation and post-surgery monitoring are essential for ensuring safety and lasting health benefits.
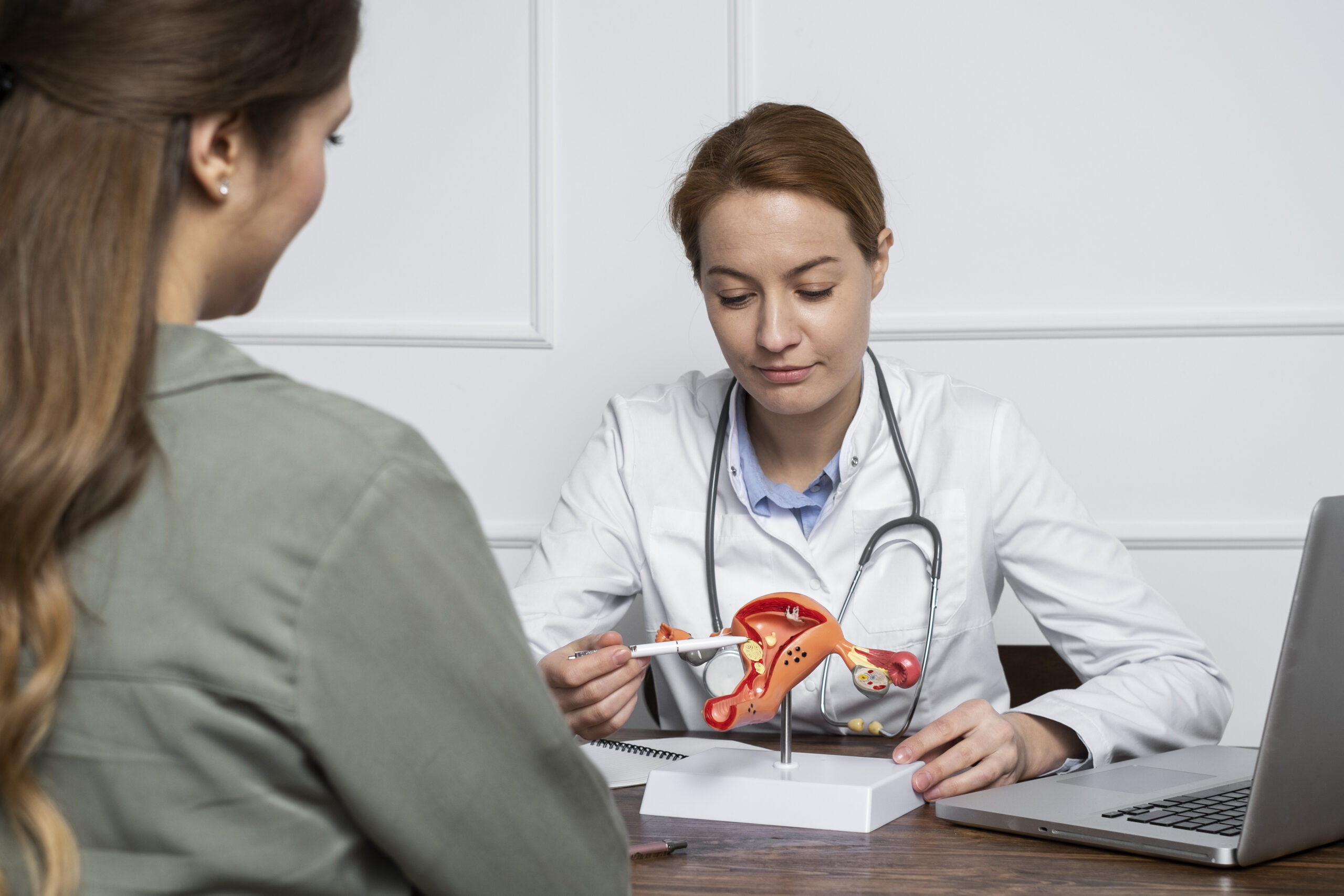

Exploring the Causes & Risk Factors of Baritric Surgey
Understanding the causes of Baritric Surgey is crucial for proper prevention, timely intervention, and overall well-being.
Genetic Predisposition
A family history of obesity or metabolic disorders can make weight loss difficult. This can lead to excessive fat accumulation despite lifestyle changes. Bariatric surgery becomes an option when other methods fail.
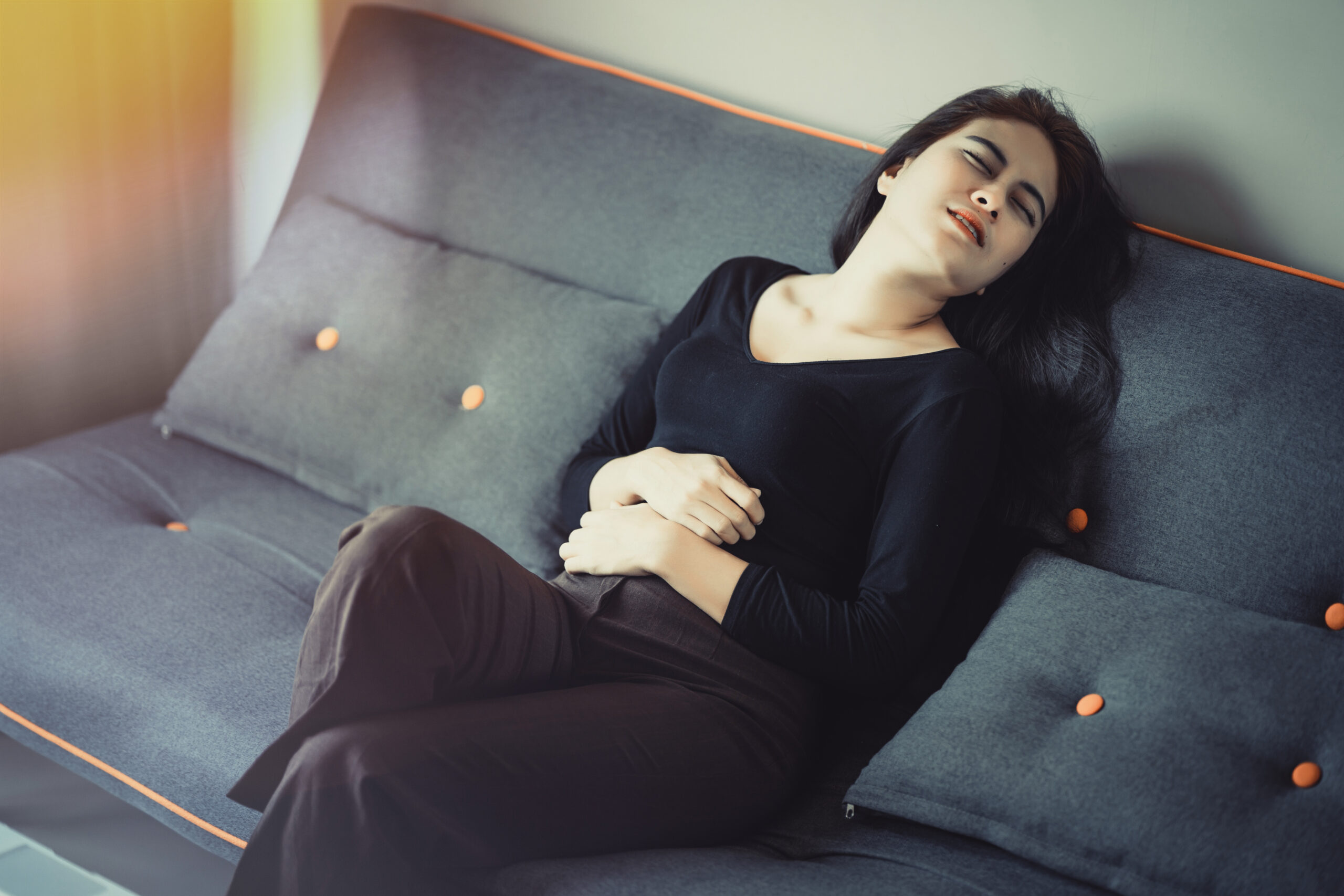
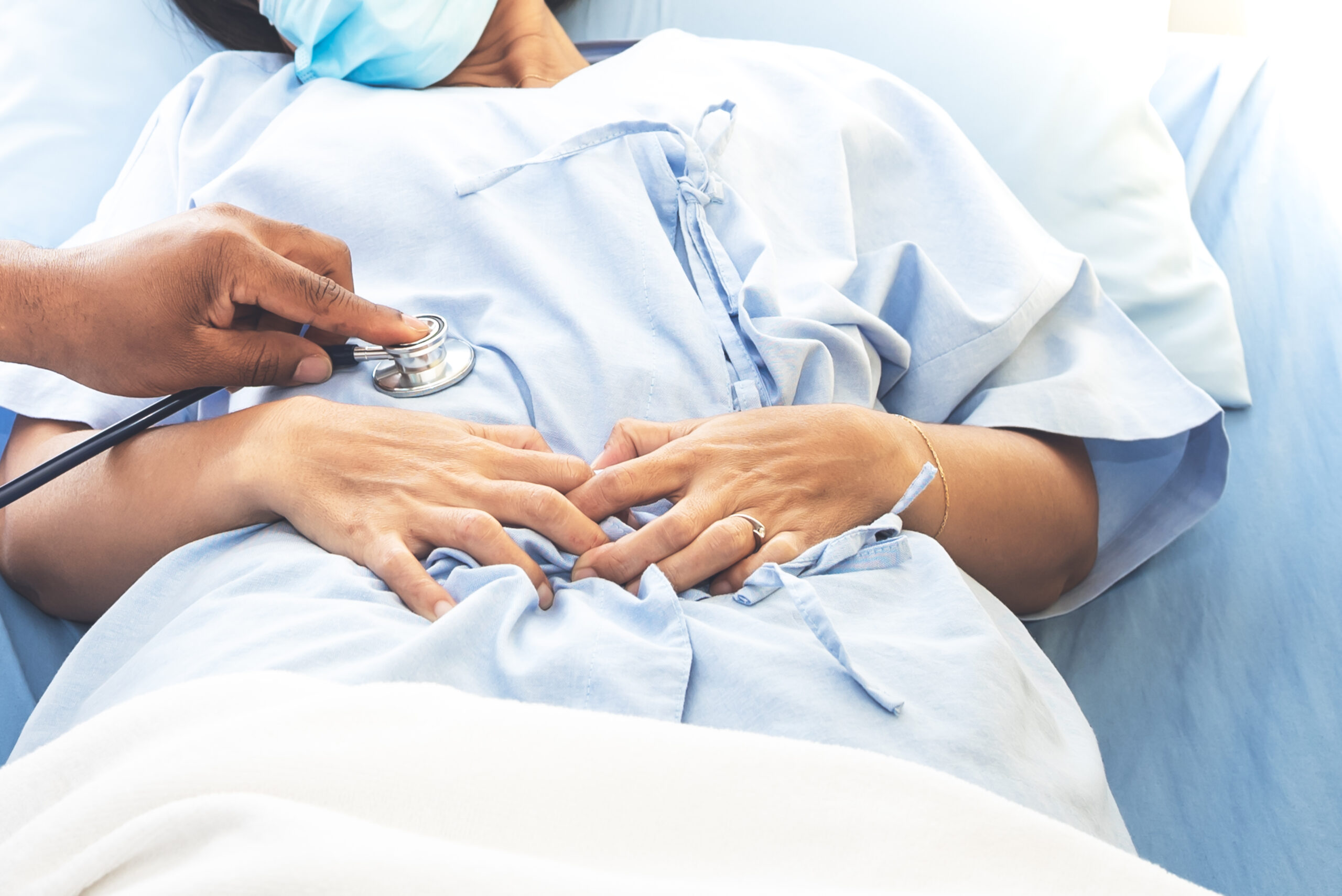

Emotional & Binge Eating
Uncontrolled eating habits, stress-related overeating, or food addiction contribute to weight gain. Emotional triggers often lead to consuming large amounts of unhealthy food. When diet management fails, surgery may be necessary.
Mobility Limitations
Joint pain, arthritis, or physical disabilities can restrict movement, leading to obesity. Lack of physical activity increases weight-related health risks over time. Surgery helps improve mobility and overall health outcomes.
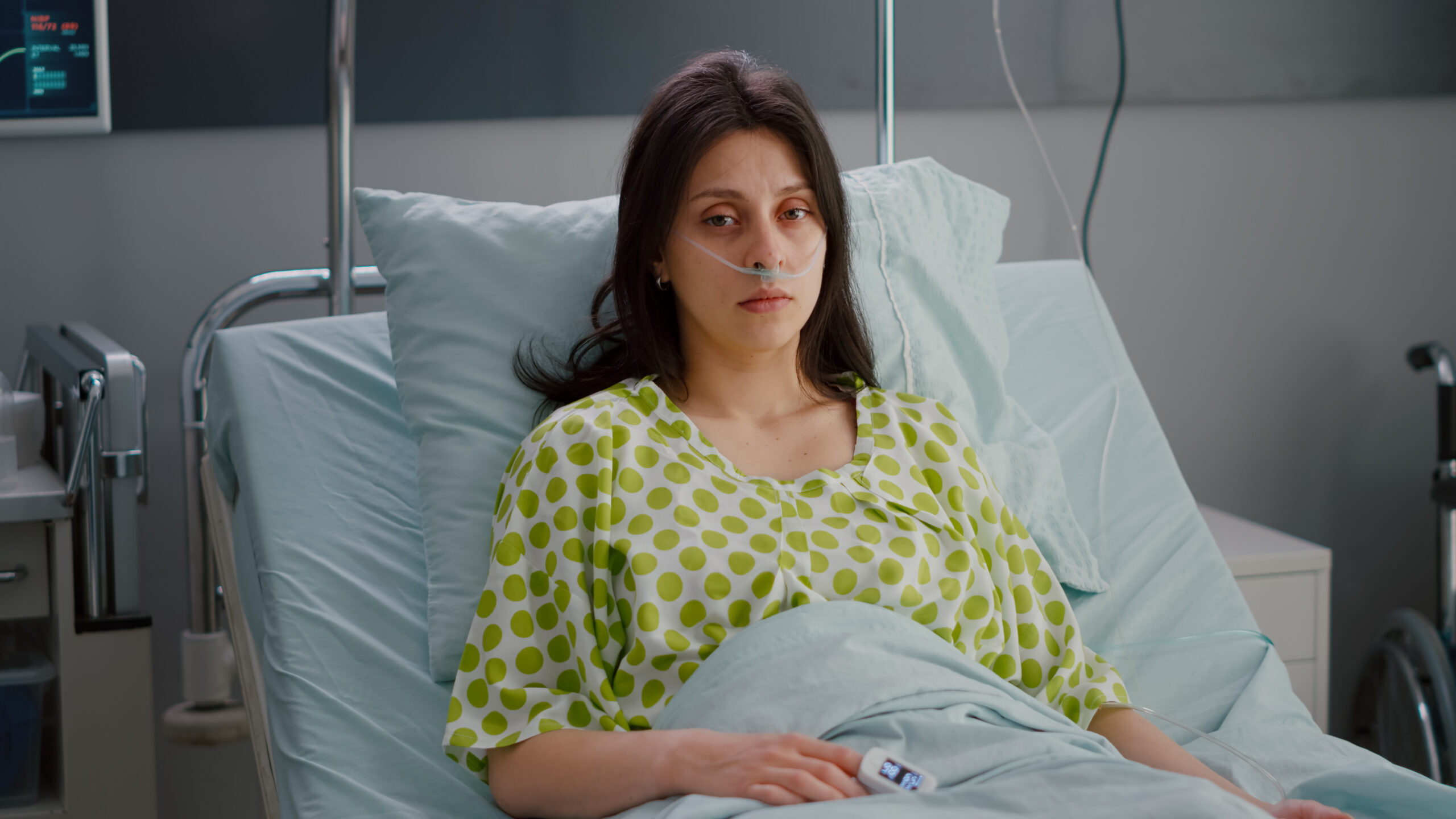
Symptoms of Baritric Surgey
Difficulty adjusting to smaller stomach capacity after surgery.
Reduced absorption of vitamins and minerals affecting overall health.
Stomach acid irritation due to anatomical changes post-surgery.
Decreased calorie intake leading to low energy levels daily.
Possible infections, blood clots, or delayed wound healing risks.
Significant reduction in body weight over a short period.

Treatment Options
- Gastric Bypass : Reduces stomach size and reroutes digestion to limit food absorption.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy : Removes a portion of the stomach to restrict food intake.
- Adjustable Gastric Banding: Places a band around the stomach to control portion sizes.
- Duodenal Switch:Combines stomach reduction and intestinal bypass for maximum weight loss.

Individuals with severe obesity (BMI ≥ 40) or those with BMI ≥ 35 and obesity-related conditions may qualify.
Common procedures include gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric banding, and duodenal switch.
Most patients resume normal activities within a few weeks, but full recovery may take several months.
A lifelong commitment to a healthy diet, portion control, regular exercise, and medical follow-ups is necessary.
It can improve or resolve obesity-related issues like diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and joint pain.
